What is RO and How RO Water purifiers works?
RO, Reverse osmosis:
Osmosis is If two solutions of different concentration are separated by a semipermeable membrane, then the solvent will tend to diffuse across the membrane from the less concentrated to the more concentrated solution.
While Reverse osmosis is a process by which any fluid is forced by applying pressure on one side of fluid, separated by semipermeable membrane. In reverse osmosis the flow will be from high concentration to low concentration through application of pressure only minute particles can only pass through this membrane depending upon the type of membrane.
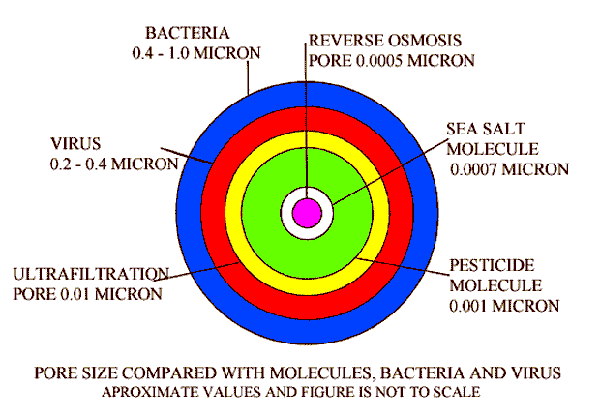
RO Reverse osmosis membranes have very fine holes called pores, through which pure water molecules can flow through but will not allow larger molecules of salt to pass through.A semipermeable membrane is a type of biological or synthetic, polymeric membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it.
The diagram shows the size of the RO membrane pore in the centre as 0.0005 microns which is slightly larger than a water molecule, so water molecules pass through an RO membrane pore.
Sodium Chloride molecule at 0.0007 micron is larger, and will not pass through the RO membrane pore. Germs, Viruses, and organic molecules which are very much larger than the RO pore cannot pass through the RO membrane pore. So when dirty water is kept under pressure on one side of the RO membrane, only pure water will pass through the RO membrane pore.
Basic Components Of A Reverse Osmosis System:
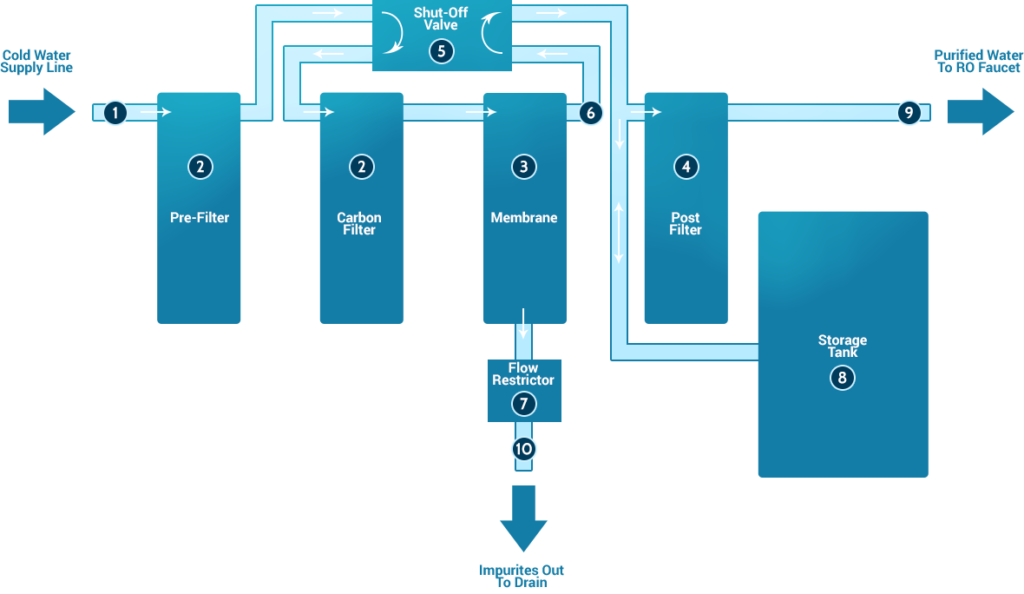
Cold Water Line Valve: Valve that fits onto the cold water supply line. The valve has a tube that attaches to the inlet side of the RO pre filter. This is the water source for the RO system.
Pre-Filter(s): Water from the cold water supply line enters the Reverse Osmosis Pre Filter first. There may be more than one pre-filter used in a Reverse Osmosis system, the most common being sediment and carbon filters. These pre-filters are used to PROTECT the RO membranes by removing sand silt, dirt, and other sediment that could clog the system. Additionally, carbon filters may be used to remove chlorine, which can damage the RO membranes.
Reverse Osmosis Membrane: The Reverse Osmosis Membrane is the heart of the system. The semipermeable RO membrane is designed to remove a wide variety of both aesthetic and health-related contaminants. After passing through the membrane, the water goes into a pressurized storage tank where treated water is stored.
Post filter(s): After the water leaves the RO storage tank, but before going to the RO faucet, the treated water goes through a final “post filter”. The post filter is usually a carbon filter. Any remaining tastes or odors are removed from the product water by post filtration “polishing” filter.
Automatic Shut Off Valve (SOV): To conserve water, the RO system has an automatic shut off valve. When the storage tank is full, the automatic shut off valve closes to stop any more water from entering the membrane and blocks flow to the drain. Once water is drawn from the RO faucet, the pressure in the tank drops; the shut off valve then opens to send the drinking water through the membrane while the contaminated wastewater is diverted down the drain.
Check Valve: A check valve is located in the outlet end of the RO membrane housing. The check valve prevents the backward flow of treated water from the RO storage tank. A backward flow could rupture the RO membrane.
Flow Restrictor: Water flowing through the RO membrane is regulated by a flow restrictor. There are many different styles of flow controls, but their common purpose is to maintain the flow rate required to obtain the highest quality drinking water (based on the gallon capacity of the membrane). The flow restrictor also helps maintain pressure on the inlet side of the membrane. Without the additional pressure from the flow control, very little drinking water would be produced because all the incoming water would take the path of least resistance and simply flow down the drain line. The flow control is most often located in the RO drain line tubing.
Storage Tank: The standard RO storage tank holds from 2 – 4 gallons of water. A bladder inside the tank keeps water pressurized in the tank when it is full. The typical under counter Reverse Osmosis tank is 12 inches in diameter and 15 inches tall.
Faucet: The RO unit uses its own faucet, which is usually installed on the kitchen sink. Some areas have plumbing regulations requiring an air gap faucet, but non-air gap models are more common
Drain line: This line runs from the outlet end of the Reverse Osmosis membrane housing to the drain. The drain line is used to dispose of the wastewater containing the impurities and contaminants that have been filtered out by the reverse osmosis membrane



