What is relay? | how relay works?
Relay is generally a switch which is same as that of switch we have at home except it contacts or breaks the circuit when electrical signal of certain condition is provided or removed from it.
Relays were initially used in telegraphs as repeaters and also had great application in first generation computers.
In todays world relays are used in each and every machine to ensure correct working and safety of machine.
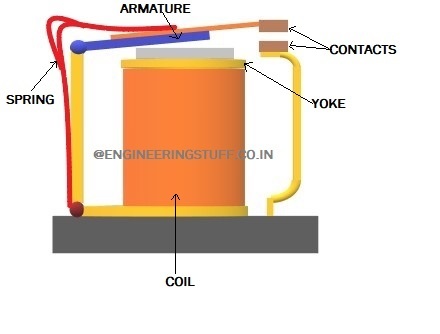
Components of Relay:
Relays is basically consist of mainly 5 parts, that is Armature, spring, yoke, coil and contacts as shown in sketch. Working of each component is as follows:
Armature: Armature is a bi metallic strip which shows magnetic effect under the magnetic field. Armature has one end joined to body and other end connected to contacts and is suspended above the yoke in such a way that way that it moves to and far from yoke under magnetic field.
Spring: One end of spring is attached to the body while other end is connected to armature. Its function is to return the armature back to place when magnetic pull on armature is over
Yoke: Yoke is the body for coil winding. It has wire winding over its body and connections for windings in and out from winding.
Coil: Coil is winding of wire around the yoke. It is generally made up of copper wire having thin layer of insulating material. Size and number of rounds of wire decides the strength and intensity of magnetic field. Rating of coil is decided according to this factor i.e. strength of signal which actuates the relay.
Contacts: Contacts are button type of part which comes in contact with movement of armature and gets seperated due to same. Contacts are made up of silver nickel alloy as it shows great resistance to electricity erosion. One contact is connected to armature and is movable while other contact is fixed at place.
Working of Relay:
Relay works on the principal of electromagnetic induction. As stated above, main function of Relay is to work as a switch, So this is how it works.
One end of electrical circuit, where switch is required, is connected to one contact and other end is connected to other contact. One electrical connection is supplied to coil. This completes the connections to the Relay.
When current is supplied to coil of relay it gets energized due to induction effect and when coil receives rated current it energizes enough to pull armature towards yoke. Armature moves movable contact towards other contact and thus completes the circuit.
When current to coil is stopped it de-energizes and armature moves back to its place due to spring action and thereafter breaking the contacts.





Recent Comments