What is LED bulb | how LED bulb works
LED Bulbs :
LED stands for light emitting diode and are currently the most widely used bulbs.
They use very less energy in comparison to Incandescent bulbs and fluorescent bulbs and also produces very less heat.
Due to these reasons LED bulbs are being replaced with Incandescent bulbs and fluorescent bulbs.
LED stands for light emitting diode and are currently the most widely used bulbs.
They use very less energy in comparison to Incandescent bulbs and fluorescent bulbs and also produces very less heat.
Due to these reasons LED bulbs are being replaced with Incandescent bulbs and fluorescent bulbs.
What is LED and how LED works?
LED’s are made up of semiconductors and semiconductors are materials whose conductive properties lies between that of conductors and insulators. It contains positive and negative charged components.
Positive component has “holes” openings for electrons and negative component has free electrons. This is called as p-n junction.
LED is comparable with general diodes with only difference being LED can emit lights in different colours. Unlike other light emitting devices in which light is produced in gaseous region, LED is SSL (solid state lighting) which means it produces light from its solid state.
It has two connections i.e. cathode and anode which are connected to p and n junctions of diode and when it is connected to voltage difference of DC direct current electrons recombines with electron holes within the device, releasing energy in the form of photons this process is called electroluminescence. The colour of light is related to the energy band gap of semiconductor.
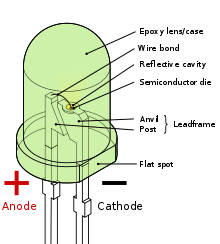
Lens as shown in above picture is made up of hard epoxy resin and is shaped hemispherical to spread light in all directions. This shell is made in such a way that photons of lights emitted by diode are spread away from the base plate.
Anvil is anode connector of semiconductor while the other one acts as cathode of semiconductor.
When LED is connected to voltage difference electrons start moving from n-region and holes start moving from p- region. then they start moving towards depletion layer electrons will stay in the conduction band and holes will stay in the valence energy band.During the recombination of electrons and holes some amount of energy is released in the form of light and heat.Near p-type region majority of light is produced which is why this area is on the outer side so that maximum of light is produced and minimum amount of light is absorbed by the system.






Recent Comments